Biometric Authentication – A Security Game-Changer for Financial Industry
Ideally, the implementation of these two directives’ requirements would be enough to enable adequate levels of protection. However, conventional security methods like passwords and PIN’s can be easily leaked or hacked, rendering them ineffective.
While it has been long possible to implement multi-factor secure authentication for mobile banking apps, in order to address contemporary security challenges, financial institutions have begun implementing biometric security. This advanced type of secure authentication verifies the identity of a customer via a distinctive physical characteristic or personal trait.
In this article, we’ll have a closer look at the benefits of biometric security in the financial industry.
The Challenges of Multi-factor Authentication
Most modern banks adopt innovative digital solutions that offer advanced transactional services to their customers. At the same time, they still rely heavily on traditional security methods, which is the reason for the global rise in financial cyber fraud. According to the Global Banking Fraud Survey by KPMG, 60% of banks globally have experienced an increased volume of fraud, and less than 25% of fraud losses were recovered.
The overwhelming majority of bank customers have grown accustomed to passwords as the standard authentication method. Unfortunately, passwords can be easily compromised by cybercriminals. The most common password hacking methods are dictionary attacks, brute-force attacks, phishing, and social engineering. Some hackers use more sophisticated methods like a rainbow table attack that threatens hashed passwords, or traffic interception, which deciphers encrypted passwords, enables unauthorized network access and allows compromising numerous accounts simultaneously. Moreover, multi-factor authentication that uses one-time passwords (OTP) via SMS can be cracked if cybercriminals implement cell phone number cloning.
All of this made banks turn to biometric security as a solution to combat fraud and safeguard customer data. 67% of banking executives invest in physical biometrics (active), like voice, fingerprint, or facial recognition, and 33 % invest in behavioral biometrics (passive).
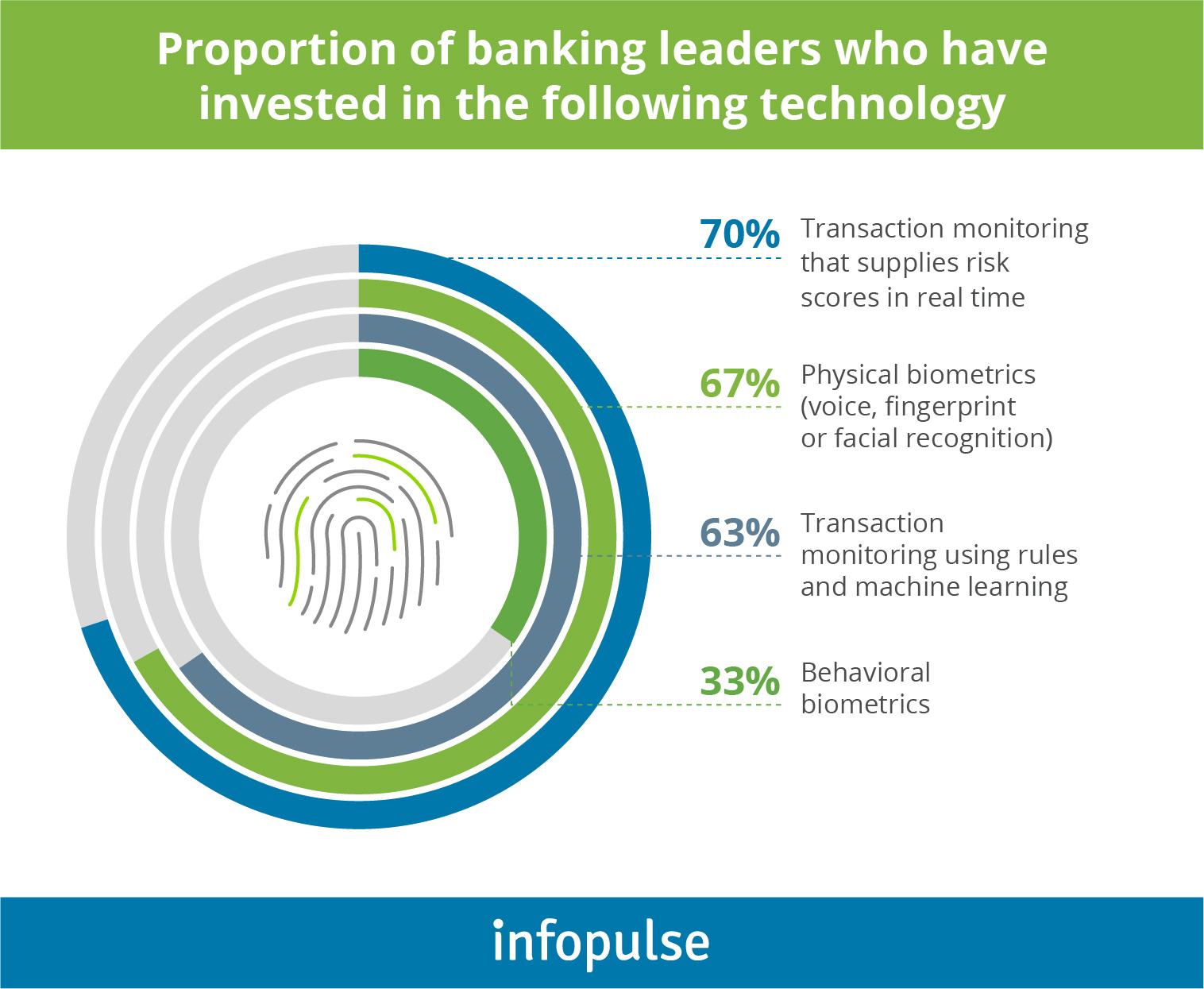
Types and Benefits of Biometrics for Financial Industry
Active biometrics are gaining popularity in the financial industry due to enhanced security and comfortable usability. The process of biometric authentication is as follows. During the first stage – enrollment – a sensor records the biometric data of the user. The data is then transformed into a binary code, encrypted, and stored within a predefined database as a template. Each time the user implements biometric authentication again, advanced AI algorithms compare the biometric data patterns against the stored template and either allow or deny access.
Four Main Types of Physical Biometrics and Their Advantages
Fingerprint Authentication
Fingerprint scanning is a swift, convenient, and reliable biometric authentication method that analyzes the unique features from the ridges and valleys of the user’s finger. Today, fingerprint authentication is a standard practice to verify identity during a financial transaction. Since 2018, MasterCard issues biometric payment cards with an embedded sensor that instantly and with exceptional precision scans, processes, and verifies the identity of the cardholder. Other examples include secure biometric ATMs and mobile payment systems like Google Pay. Most importantly, fingerprint biometrics are extremely hard to forge or duplicate, which excludes the possibility of unauthorized access to financial assets.
Eye Print Scanning
Eye print scanning is another efficient biometric authentication method that has extremely low chances of false matching. It may be performed in various forms, specifically by scanning different parts of the eye, like the iris, retina, or sclera. The retina and sclera authentication process involves the scanning of the person’s unique eye blood vessel patterns. These biometric measures are rarely implemented because they require a very close scanning of the eye – a process not as user-friendly as one would think. For now, iris scanning remains the most convenient eye print authentication method. The user will precisely be authenticated even if they wear contact lenses or eyeglasses; besides the technology has already arrived to smartphones as well. Banks are now actively adopting eye print authentication solutions; for example, Wells Fargo CEO Mobile banking application features a quick and easy login via eye print scanning.
See how Wells Fargo solution leverages eye print authentication to enable access to the company’s financial data:
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition is based on two major methods: the geometric recognition that scans distinguishing facial features, and the statistical photometric approach, which distributes the image data into values and compares them to the templates stored in specific databases to detect divergence. 3D Facial recognition is a very reliable authentication method because it is not affected by changes in lighting or the person’s makeup, and can identify the user from various viewing angles, including a profile view. Modern banks implement facial recognition to streamline customer identification during the mobile KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance process.
Voice Authentication
Voice is a unique attribute of each person, just like the fingerprint or iris. Individual respiration, soft-tissue cavities, and specific mouth and jaw movements produce a voice pattern with distinctive pitch, dynamics, and intensity, altogether forming an individual voiceprint.
There are two major types of voice authentication:
- Text-independent – authentication is performed by analyzing any speech content delivered by the user.
- Text-dependent – the system requires the user to say a fixed or randomized passphrase.
Voice biometrics are highly efficient because they cannot be impersonated. The system does not confuse the user’s natural speech with a recording, and background noises do not affect its performance.
One of the primary benefits of voice biometrics is its user-friendliness since voice authentication is contactless, convenient and is easily accessible via smartphones. Besides, voice authentication can be integrated with other devices, like smart vehicles or home appliances. Furthermore, by implementing voice authentication banks may improve cost-efficiency, since it reduces the time spent by each support agent to verify the user, resulting in additional overhead savings.
Behavioral Biometrics
On top of that, another high-end method of biometric security is emerging – the behavioral or so-called passive biometrics.
Passive biometrics are based on a concealed AI-driven security suite that consistently authenticates the user by analyzing different ways of interaction with their device, including smartphone or tablet keystrokes, swiping patterns, and scrolling speed. The data is accurately reviewed by a multitude of parameters, which eliminates the chances of unauthorized access. Banking apps that feature passive biometrics create continuous authentication and frictionless user experience. Having the ability to identify the inherent behavior of the user in real-time, banks can instantly detect malware bots, fraudulent transactions, and significantly reduce the rates of false positives.
A prominent use case of passive biometrics is MasterCard’s NuData Security, which utilizes four levels of security, efficiently excluding customer account takeovers and automated cyber-attacks. Once the MasterCard’s solution was adopted by numerous large-scale US banks, it was revealed that 30% of their login traffic was generated by malicious attacks targeted at customers’ accounts.
Conclusion
According to the MarketsandMarkets report, the biometric system market will almost double in growth by 2024. Such growth predictions can be attributed to distinct advantages of implementing biometrics, which are robust security in omnichannel banking, improved privacy, and enhanced customer experience.
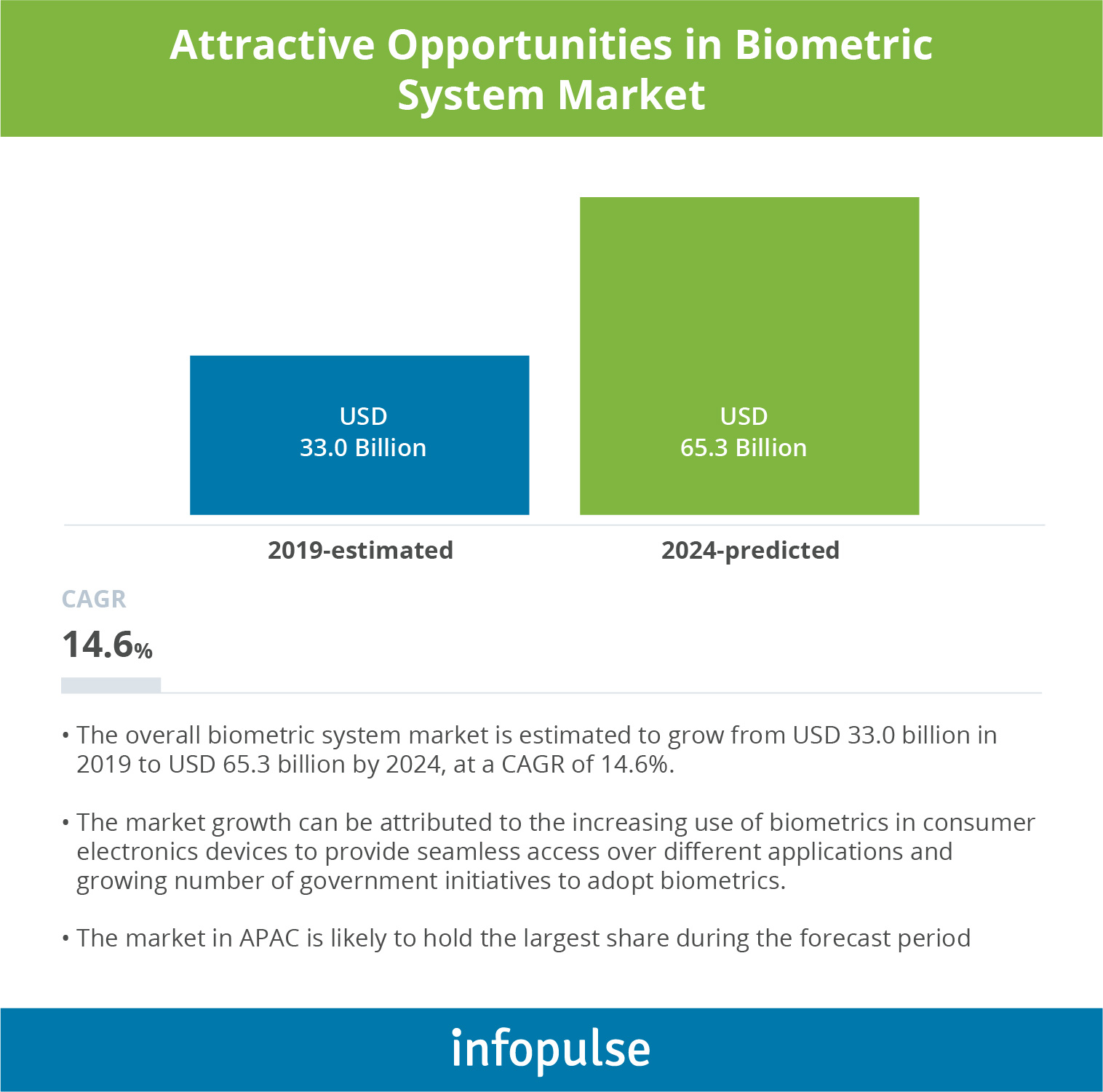
Amid the digital disruption, safe identity authentication is one of the major challenges that the financial industry has to address. Global fraud rates are rising, and the financial sector can no longer rely on conventional security methods like passwords, which can be easily compromised by cybercriminals.
The adoption of active or passive biometric authentication solutions can reinforce financial security systems, benefit cost-efficiency, and create an exceptional user experience.
If you are looking for an experienced digital service provider, who can help you with the adoption of biometric authentication solutions, feel free to contact the Fintech experts of Infopulse.

![CX with Virtual Assistants in Telecom [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/280x222-how-to-improve-cx-in-telecom-with-virtual-assistants.webp)
![Generative AI and Power BI [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-generative-AI-and-Power-BI-a-powerful.webp)
![AI for Risk Assessment in Insurance [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/aI-enabled-risk-assessment_280x222.webp)
![Super Apps Review [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-introducing-Super-App-a-Better-Approach-to-All-in-One-Experience.webp)
![IoT Energy Management Solutions [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-iot-energy-management-benefits-use-сases-and-сhallenges.webp)
![5G Network Holes [Thumbnail]](/uploads/media/280x222-how-to-detect-and-predict-5g-network-coverage-holes.webp)

![How to Reduce Churn in Telecom [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-how-to-reduce-churn-in-telecom-6-practical-strategies-for-telco-managers.webp)
![Automated Machine Data Collection for Manufacturing [Thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-how-to-set-up-automated-machine-data-collection-for-manufacturing.webp)
![Money20/20 Key Points [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-humanizing-the-fintech-industry-money-20-20-takeaways.webp)