How AI-Driven Virtual Assistants Help Telcos Enhance Their Customer Experience
Low customer satisfaction inevitably leads to churn and increases customer acquisition costs (CAC). Digital over-the-top (OTT) platforms are also increasing their penetration rate in the media market (by over 132% in the UK and by more than 135% in Canada, for example), eroding media profits from traditional pay TV services (cable and satellite) offered by telecoms for years.
Soundly, telecom leaders realize the problem: 73% see improving CX as a top priority for this year, according to McKinsey. Chatbots have been widely adopted in the customer support function. Yet, until recently, their capabilities were rather limited, offering helpful assistance in only a fraction of cases.
The recent advances in generative AI ignite new possibilities for improving the customer support function. Powered by large language models (LLMs) like GPT, BERT, and LLAMA, virtual assistants can better recognize different speech patterns. Moreover, thanks to fine-tuning techniques like retrieval augmented generation (RAG), AI virtual assistants can also contextualize responses using information from connected corporate databases (e.g., customer service policies) or business analytics systems. These advances enable a range of new customer-centric improvements in the telecom sector.
How Telecom Companies Use AI-Powered Virtual Assistants
Telecom leaders are eager AI adopters, with 48% citing “enhancing customer experiences” as the main goal for using the technology, according to a 2024 NVIDIA survey. Over half of leaders (57%) aim to deploy generative AI to improve customer support and another 57% — to improve employee productivity.
Our team has identified the key customer experience problems telecoms can effectively solve with various AI technologies.
Problem
Solution
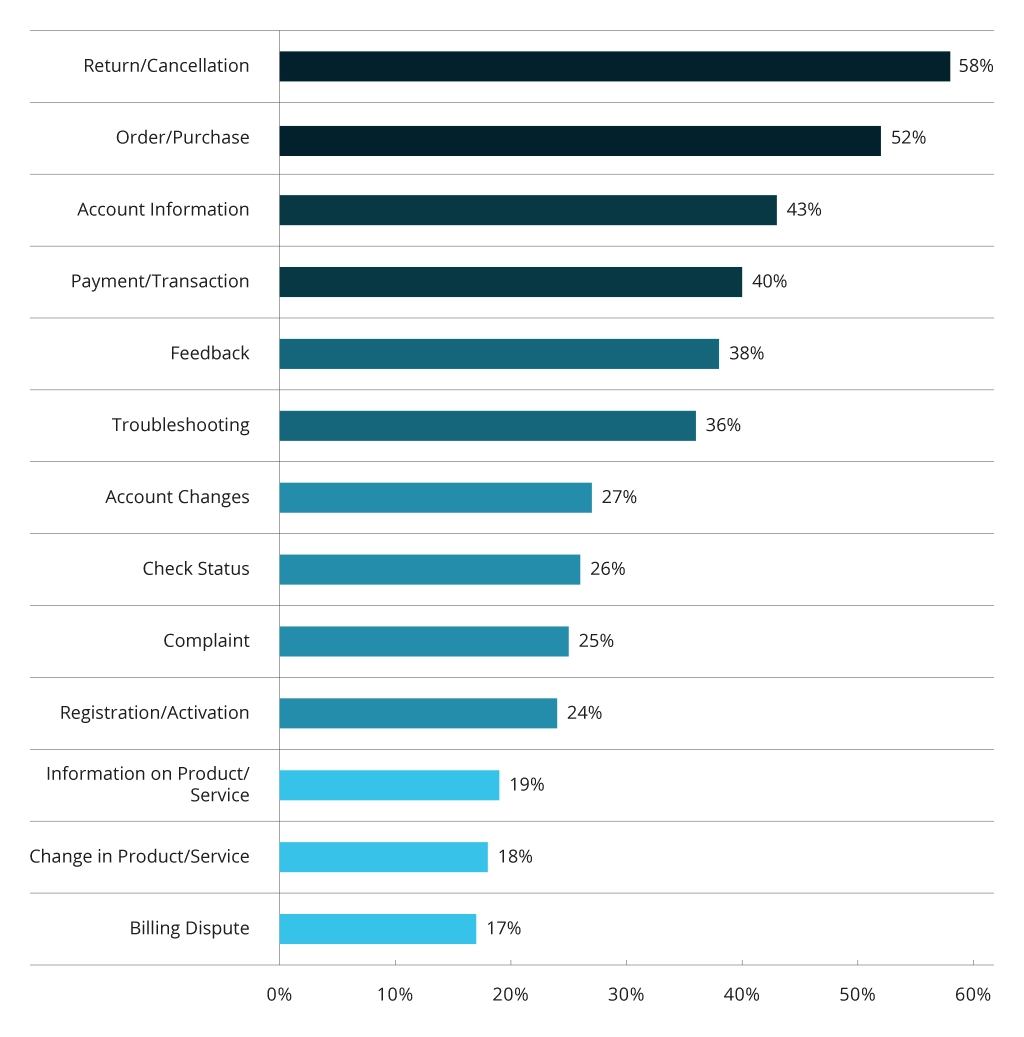
Long phone and chat wait times due to high request volumes
In-app and on-site AI virtual assistants, pre-trained on corporate data for self-service using RAG
Language barriers/lack of multilingual staff
Open-source, multi-language LLM for high-quality machine translations
Missed sales and cross-sales opportunities
Personalized in-app product recommendations, using predictive analytics and machine learning
Siloed or inaccessible customer insights
Automatic transcription and sentiment analysis ML. Advanced contextual data search with an internal LLM
Impersonal communication
An LLM, fine-tuned to mimic the corporate tone of voice
High operating costs for a large support function
Employees, empowered with internal assistants for information look-up, plus text, video, and image reply generation
Personalized Customer Engagement
Ensuring high customer lifetime value (CLV) is one of the key objectives for telecom companies. Yet, with hard-nose market competition, and poor support levels, many end up acquiring ‘value destroyers’. A new study found that 20% of newly acquired telco customers have a negative lifetime value and drain around 40% of company profits every year. Even though the remaining 80% of new customers generate a profit, their value varies widely.
Virtual AI assistants help plug revenue leaks, caused by poor customer support and lack of proactive engagement. Internal generative AI assistance can effectively parse large volumes of data, supplying your customer success, sales, and marketing teams with aggregated insights. For example, an AI assistant can help locate customer cohorts that frequently make international calls and group them for a personalized outreach campaign. Generally, AI can support a wide range of customer analytics use cases in telecom — from lookalike audience modelling for targeted ad campaigns to churn prediction and network experience optimization.
At the front end, in-app AI virtual assistants can also proactively engage with consumers, offering personalized deals, promotions, or plan changes, based on their usage patterns. For instance, Indonesian Telkomsel incorporated AI capabilities into its chatbot by using Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service. The upgraded assistant Veronika can assess customer needs and recommend suitable product packages, supply product knowledge, and speed up issue resolution, according to the company’s spokesperson. The virtual assistant handles a large volume of general customer inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex cases.
The advantage of AI-powered customer solutions is that they can provide customer inquiry triage, offering self-resolution in simple cases and fast-tracking urgent matters to the most qualified agents. With access to historical customer data, the algorithm, for example, can be programmed to speed up repeated requests from the same customer about the same issue (e.g., poor Internet service) and automatically suggest compensation (e.g., a one-time 15% discount), based on the pre-programmed policies. Effectively, with AI chatbots telcos can make each customer feel heard and valued without running a large customer support workforce.
Multilingual Support
The first generation of machine translation systems was trained on bilingual text pairs (e.g., English to Spanish) to translate one language to another. Due to this, many models struggle to interpret synonyms or slang and provide inconsistent outputs. LLMs are trained on a much larger corpus of texts to predict the next word in the phrase. Such an approach enables a greater contextual understanding of the speech.
Since many LLMs are open-source, developers can further fine-tune them to provide better translations in specific languages. Fine-tuning involves training it on a smaller, task-specific dataset (e.g., a set of common industry terms in Japanese) to improve its performance. For example, BLOOMChat, an open, multilingual chat application, demonstrated 42% better performance than GPT-4 across 6 languages in a human preference study.
South Korea SK Telecom, for example, launched a multi-lingual AI call assistant to provide real-time interpretation during calls. The system supports Korean, English, Japanese, and Chinese translation, activated with one tap via the carrier’s mobile app. Seamless multi-language translations do not only improve customer satisfaction, but also help expand to new markets faster and more cost-effectively. Language proficiency ensures that non-native speakers receive the same quality of service, which is crucial for global or national operators serving diverse populations. Customers who might not be proficient in the primary language of the region where they reside can interact comfortably in their own native language. This accessibility is particularly important in regions with high levels of immigration or countries with multiple official languages.
Faster Issue Resolution
The emerging swarm of AI Copilots helps streamline a wider range of knowledge processes — document lookup, voice call transcription, data wrangling, and code troubleshooting among others. Many of these capabilities can help customer support agents investigate and resolve customer cases with greater efficiency.
Azure Open AI, combined with RAG, open-source large language models can be provided with access to corporate databases — support policies, technical manuals, service level agreements, billing details, and any other training documents agents use in their work. Instead of opening multiple tabs, agents can send conversational queries to a Copilot and receive contextual guidance for troubleshooting. AI copilots can also generate checklists, cross-check information, and even generate photo or video walk-throughs to instantly send to customers. And, what's very important from the security and data privacy point of view, the data remains stored in the data source and location you designate. No data is copied into the Azure OpenAI service.
For instance, South African telco group MTN developed SiYa, an AI-powered copilot available via the Microsoft Teams app. Connected to the internal knowledge base, SiYA can instantly provide up-to-date information on a wide range of topics, from policy updates to standard operating procedures. The group’s CEO believes that SiYa will be “instrumental in shaping the future of customer engagement at MTN.”
Find out more about the ways AI virtual assistants can troubleshoot an array of technical issues as first-line support in a dedicated article.
Automated Feedback Collection and Insightful Data Analytics
AI-driven virtual assistants are capable of gathering and analyzing extensive data from customer interactions, which are crucial for strategic decision-making. This data allows revealing trends, customer preferences, and common issues. As a result, you can further improve product development, marketing strategies, and customer service. By incorporating multichannel integration, telecom companies can also enable comprehensive analytics about customer behaviour and preferences across all communication platforms. This will also enhance the AI per se since insights on interactions in one channel can help improve interactions in another one.
Virtual assistants can also automate the process of collecting feedback on all customer interactions and service experiences. Since the feedback is gathered systematically and consistently, telecoms can quickly identify and address their concerns, also providing real-time insights into customer satisfaction. For telecom operators, these insights are crucial for staying competitive and responsive to market needs.
Barriers to Using AI-Driven Virtual Assistants
AI assistance can drive substantial improvements in standard operating workflows, helping companies elevate their service levels. However, leaders are held back by a mixture of technical challenges and budgetary constraints:
- Tech skills shortages: 34% of telecom leaders say there are too few data scientists and machine learning engineers to support their AI initiatives. Given that AI adoption requires cross-functional expertise, telecoms build strategic partnerships with technology partners in that field. Infopulse has been a strategic partner for BICS since 2010, helping the company implement a range of network service fulfilment and assurance projects and OSS/BSS application modernization projects.
- Hard-to-measure ROI: Quantifying the value of an innovative project is challenging as there are no reference benchmarks. The best approach to measuring the impacts is to conduct a cost-benefit analysis that establishes a data-backed present-day baseline and future target KPIs that can be influenced by AI adoption. Then you can measure the cost of initial investment and ongoing operational costs against the value of future improvements.
- Data privacy and security. To avoid accidental disclosures and minimize the risks of cyber-attacks, we recommend implementing privacy-preserving techniques for protecting AI systems, such as homomorphic encryption, differential privacy, secure multiparty computation, and federated learning techniques.
Final Thoughts
AI can help telecom companies unlock extra operational and customer insights and translate these into measurable improvements in NPS scores. Virtual assistants continuously evolve through AI, offering increasing value to telecom operators and their customers, but also require careful management regarding privacy, bias, and transparency.



![CX with Virtual Assistants in Telecom [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/280x222-how-to-improve-cx-in-telecom-with-virtual-assistants.webp)
![AI in Telecom [Thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-ai-in-telecom-network-optimization.webp)

![Telecom Tech Trends [Thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-what-is-hot-in-telecom-nine-tech-trends-to-impact-the-industry-in-2024.webp)




